The parts of speech are the building blocks of the English language. This Simple Guide to the Parts of Speech will help you understand how each part works. Understanding these categories helps us construct sentences that are clear, meaningful, and grammatically correct. Whether you’re a student or someone looking to improve your communication skills, mastering the parts of speech is essential. Here, we’ll explore the eight main parts of speech with examples to simplify the concept for you.
Simple Guide to the Parts of Speech
Understanding the parts of speech is essential for mastering English grammar. In this guide, we’ll explore each part—nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections—and show you how they work together to form meaningful sentences. Whether you’re a beginner or looking to brush up on your skills, this guide provides everything you need to enhance your language proficiency.
1. Nouns
Nouns name people, places, things, or ideas. They form the subject or object of a sentence.
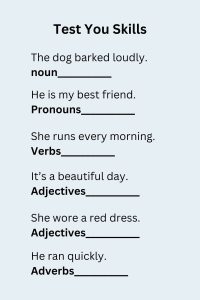
- Example: The dog barked loudly. (dog is a noun.)
- Example: She has a great idea. (idea is a noun.)
2. Pronouns
Pronouns replace nouns to avoid repetition.
- Example: He is my best friend. (He replaces a specific person’s name.)
- Example: They went to the park. (They replaces multiple individuals.)
3. Verbs
Verbs express actions, occurrences, or states of being.
- Example: She runs every morning. (runs is an action verb.)
- Example: I am happy today. (am is a state of being verb.)
4. Adjectives
Adjectives describe or modify nouns and pronouns, adding details about qualities or quantities.
- Example: It’s a beautiful day. (Beautiful describes the day.)
- Example: She wore a red dress. (red describes the dress.)
Read More:
- 7 Must-Know Greetings & Introductions in Spoken English (Mistakes to Skip)
- Opposite Words – 200+ for Better English Communication
5. Adverbs
Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They often tell how, when, where, or to what extent something happens.
- Example: He ran quickly. (quickly modifies the verb ran.)
- Example: The movie was very interesting. (very modifies the adjective interesting.)
6. Prepositions
Prepositions show relationships between nouns (or pronouns) and other parts of the sentence.
- Example: The book is on the table. (on shows the relationship between the book and the table.)
- Example: She walked through the park. (through shows movement.)
7. Conjunctions
Conjunctions connect words, phrases, or clauses.
- Example: I wanted to go, but I was too tired. (but connects two clauses.)
- Example: Bring your coat and scarf. (and connects two nouns.)
8. Interjections
Interjections are short exclamations that express emotions.
- Example: Wow! That’s amazing. (Wow! expresses surprise.)
- Example: Oops! I dropped my phone. (Oops! shows a mistake.)
Why Understanding Parts of Speech Matters
Learning the parts of speech gives you the tools to form correct sentences and improve your writing and speaking skills. For instance, knowing how to use adverbs effectively can make your descriptions more vivid, while understanding prepositions ensures clarity in complex sentences.
Final Thoughts
Mastering the parts of speech is the first step toward mastering the English language. Start by identifying these categories in everyday sentences and practice using them in your writing. With time, you’ll notice a significant improvement in your communication skills. As the saying goes, “Good grammar is the foundation of great communication.”